Statistics
Population
- The 1994 census found there to be 4.139 million people
living in Jordan. The census previous to this one was in 1979 when the
population was found to be 2.125 million.
|
 |
- 90% of Jordan's population lives in the North (Amman and
northwards), on 15% of Jordan's land.
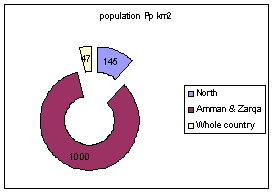
- The population density in Jordan as a whole is 47
persons/km2; the population density in the
North is 145 persons/km2 and the population density in Amman and
Zarqa is 1000/km2.
- The crude birth rate is 33.5/1000 persons and the crude
death rate is 4.25/1000 persons. This makes for a natural population increase of
2.9%.
- A majority of the population lives in an urban areas:
79% live in an urban area while 21% live in a rural area.
- 40% of the population is below the age of 15 years.
Marriage and Fertility
- For men, the mean age at marriage has remained steady over
the past forty years at approximately 25 years of age.
- For women, the mean age of marriage has steadily risen from
17 to above 20 years of age. More younger women achieving higher
levels of education is causing the overall age at marriage to rise.
- About 25% of marriages are between first cousins; the most
popular of these marriages is the father's brother's son marriage (ibn
'amm-bint 'amm). Another one-fifth of marriages are made within
the same clan or hamulah.
- Totale Fertility Rate (TFR) for women in Jordan is
declining, from above 6 in 1985-6 to 4.3 in 1997. In reagrds of other
Middle Eastern/North African countries, Jordan ranks 10 out of 19 in terms
of its TFR.
Mortality
- Infant mortality (below the age of 1 year) and child
mortality (below the age of 5 years) are both very low for a developing
country. Infant mortality is 28.1 deaths/1000 infants and child
mortality is 32 deaths/1000 children under 5.
Education
- Illiteracy rate is about 14% for the population as a
whole. This is 1/2 of what it was 15 years ago. The literacy rate is
much better in Jordan than other developing countries and Arab States.
- Elementary schools are within walking distance of 80% of
all households.
- 95% of all children eligible for elementary school are
currently enrolled. 70% of those eligible in the secondary school
population are enrolled.
- The greatest gains in education have been for females, and
girls actually have higher enrollment than boys at some stages of education.
- There are 24 private and public four-year universities in
Jordan. There are also 50 two-year colleges, public and private,
throughout the country.
- One of the reasons education is so important in Jordan is
because this country is limited in its natural resources, with most people
working in the services sector.
Health
- 67% of all households have at least 1 doctor, health center
or hospital within a 5 - 10 minute walking distance from their homes.
- Approximately 53% of all people are covered by health
insurance.
- Military health insurance is the most common with 43% of
those insured covered by military insurance. Government insurance
covers 40% of those insured, and private and UNRWA each cover 9% of those
insured.
- The ratio of hospital beds available throughout the country
to Jordanian residents is 1 bed/920 persons. In reality, we have more
hospital beds than can be filled.
- Smoking. 24% of the adult population smokes
regularly; 3-4% smoke from time to time. 44% of men smoke daily; 5% of
women do the same.
Housing and Infrastructure
- Most urban and rural households have water piped into their
living quarters.
- 99% of all households have electrical power services.
- 81% of all households have a paved road to the house.
Household Wealth and Income
- Median income for Jordan is approximately 2000 JD per year.
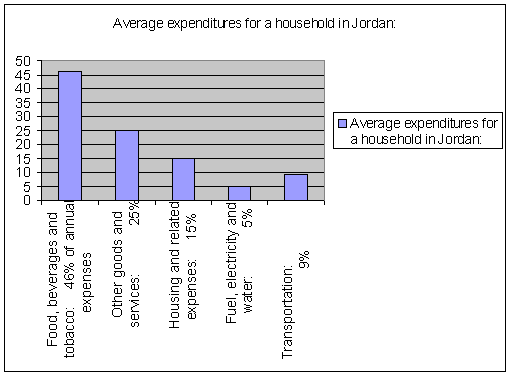
- Average expenditures for a household in Jordan:
- Food, beverages and tobacco: 46% of
annual expenses
- Other goods and
services:
25%
- Housing and related expenses: 15%
- Fuel, electricity and
water: 5%
- Transportation:
9%
|
 |
- Generally, richer households are in urban areas and a
clustering of low income households in rural areas.
- Almost 40% of Jordanian households have access to
agricultural land or glarden plots.
- 10% of households have no economically active member.
- 7% of households have a main provider who is umemployed.
Labor Force
- 17% of economically active persons are women.
- The public sector (the government) is the largest employer
in the country, and employs the majority of persons with higher
education. Although low-skilled occupations which are usually a sign
of low education, they included 8% of men with higher education implying an
abundance of people with higher education.
Public Life
- 6 of 10 Jordanians above the age of 20 have ever voted in
national or municipal elections, with only a minority of difference between
the sexes.
- About 2 times as many men oppose female involvement in
political and associational life as compared to women. But,
researchers' main conclusion is that there is a general 'psychological'
barrier against female public and political participation in Jordanian
society.
Land
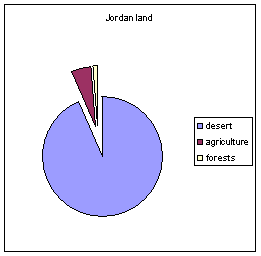
- 4 million dunums, or 4% of Jordan's land, is cultivated for
agricultural purposes.
- 71 million dunums of Jordan's land is desert. That is
nearly three-quarters of the country.
- 760,000 dunums are forests
|
 |
- 20% of all income earned in Jordan comes from agriculture.
- 6% of the labor force works in agriculture.
Wildlife
- There are four different natural regions in Jordan, each
one has a specific type of animal life. These regions are the:
Mediteranean Region, the Steppe Region, the Eastern Desert Region and the
Wadi Araba/Jordan Valley Region.
- Years ago, Jordan was inhabited by animals now extinct from
here--such as giraffes, elephants, and tigers. We know of their
presence from fossils, and Safayatic and Wadi Rum inscriptions.
- There were local animals that used to live in Jordan but
were made extinct or migrated because of hunting, a lack of food, and
deforestation.
- Some of these animals that left, or died-off, were
reintroduced to Jordan. Examples are the Oryx, Onegan, Fallow and Roe
deer, and the Ostrich. As part of the reintroduction of these animals,
the government created 8 natural animal reserves.
- Currently, there are 97 different kinds of reptiles in
Jordan and 375 types of birds--275 of these are migratory which appear in
Jordan only during certain times of year.
- There are 75 different kinds of mammals.
- There are nearly 400 different types of fish in
Jordan. Most of these fish are salt water fish living in the Red Sea,
but 23 kinds are found in the Jordan River and dams.
Many of the above facts were taken
from:
Hanssen-Bauer J, J Pederson, AA
Tiltines. 1998. Jordanian Society. Living Conditions in the
Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan. Fafo report no. 253. Oslo: Fafo.



